Spring Boot2 核心技术与响应式编程
Spring Boot2 核心技术与响应式编程
第一季:SpringBoot2 核心技术-基础入门
01、Spring 与 SpringBoot
1、课程介绍

**本视频文档地址:**https://yuque.com/atguigu/springboot
**本视频源码地址:**https://gitee.com/leifengyang/springboot2
2、Spring 生态圈
Spring 可以做什么:Microservices(微服务)、Reactive(响应式编程)、Cloud(分布式)、Web apps、Serverless(无服务开发、函数式开发)、Event Driver(事件驱动)、Batch(批处理)
2.1 SpringBoot 目的、优点、缺点
3、SpringBoot 大时代背景
3.1 微服务
3.2 分布式
3.3 云原生
4、如何学习 SpringBoot
4.1 官方文档
02、SpringBoot2 入门
1.系统要求
- Java8&兼容 Java14
- Maven 3.3+
- idea 2019.1.2
1.1 maven 设置
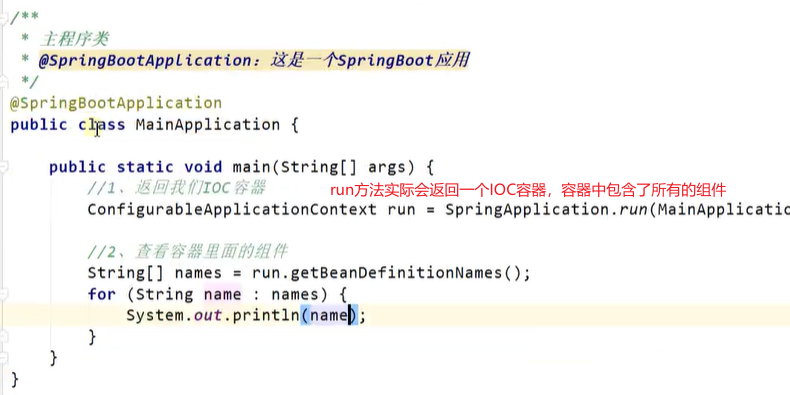
2.HelloWorld
需求:浏览器发送/hello 请求,相应 Hello
参照官方文档 4.Deceloping Your First Spring Boot Application
2.1 创建 Maven 工程
2.2 引入依赖
2.3 创建主程序
2.4 编写业务
2.5 测试
2.6 简化配置
- application.properties
- 可以配置哪些东西,参考官方文档:Application Properties
2.7 简化部署
添加依赖,打成jar包,clean、package注意点:取消掉 cmd 的快速编辑模式,不然鼠标点一下命令行窗口,就停止运行了
03、了解自动配置原理
1.SpringBoot 特点
1.1 依赖管理
父项目做依赖管理 几乎声明了所有开发中常用的依赖版本号,自动版本仲裁机制;也可以自定义修改版本
开发导入 starter 场景启动器
- 只需要导入 spring-boot-starter(场景启动器)
- 参考官方文档 using-spring-boot,spring-boot-starter-*。就代表某种场景,这个场景的所有常规需要的依赖都会自动引入。 右键-Diagrams-Show Dependencies:分析依赖树
- 所有场景启动器最底层的依赖:SpringBoot 自动配置的核心依赖 spring-boot-starter
无需关注版本号,自动版本仲裁 引入非版本仲裁的 jar,要写版本号
1.2 自动配置
自动配好 Tomcat
- 引入 Tomcat 依赖
- 配置 tomcat
自动配好 springMVC 在主程序类中
- 引入了 SpringMVC 全套组件
- 自动配好 SpringMVC 常用组件(功能):
- 在 spring springmvc 整合中要写一大堆,最先配置的是 dispatcherServlet,解决字符乱码要配置 characterEncodingFilter(返回中文时候不乱码),视图解析器……
自动配好 Web 常见功能,如:字符编码问题
默认的包结构
- 在 spring springmvc 中要配置包路径扫描
- 主程序所在的包及其下面所有子包都可以默认扫描,无需配置以前的包扫描
- 也可以自己配置,通过注解配置默认扫描包 @SpringBootApplication(scanBasePackages="")、@ComponentScan
各种配置拥有默认值
- 默认配置最终都是映射到某一个类上的
- 配置文件的值最终会绑定某个类上,这个类会在容器中创建对象
- 要用到这个值的时候,在 springboot 底层拿到这个类的对象,提取它的默认值就行了
按需加载所有自动配置项
- 非常多的场景,引入哪个场景,这个场景的自动配置才会开启
- SpringBoot 所有自动配置功能都在 spring-boot-autoconfigure 包里面
2、容器功能
2.1 组件添加
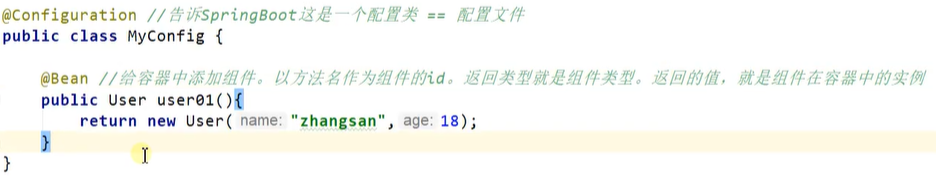
2.1.1 @Configuration
Spring:在 spring 中给容器添加组件需要创建 spring 配置 xml 文件,使用 bean 进行配置

SpringBoot:使用 @Configuration 创建一个配置类(本身也是一个组件),等同于配置文件,使用 @Bean 标注方法添加组件(默认是单实例)
- @Configuration 有一个属性 proxyBeanMethods=true:代理 bean 的方法。可以直接调用配置类的方法获取组件,但外部无论对配置类中的这个组件注册方法调用多少次,获取的都是之前注册容器中的单实例对象
- proxyBeanMethods=true:因为配置类是代理对象,代理对象调用方法,SpringBoot 总会检查这个组件是否已经有了,有的话就会直接取该组件
- SpringBoot2 的一大更新,配置类的 Full 模式(proxyBeanMethods=true)和 Lite 模式(proxyBeanMethods=false),解决的问题是组件依赖
- 配置类 组件之间无依赖关系,用 Lite 模式加速容器启动过程,减少判断
- 配置类 组件之间有依赖关系,方法会被调用得到之前的单实例组件,用 Full 模式
2.1.2 @Import
在配置类上使用,@Import({User.class, DBHelper.class}),给容器中自动创建出这两个类型的组件,默认组件的名字就是全类名
2.1.3 @Conditional
条件装配:满足 Conditional 指定的条件,则进行组件注入
Ctrl+H 打开继承树
2.2 原生配置文件引入
2.2.1 @ImportResource
在配置类上 @ImportResource("classpath:beans.xml")导入 Spring 的配置文件
2.3 配置绑定
将 JavaBean 与配置文件绑定:
- 在 JavaBean 中使用 @Component+@ConfigurationProperties:将组件实例中的值跟配置文件绑定,prefix 代表前缀
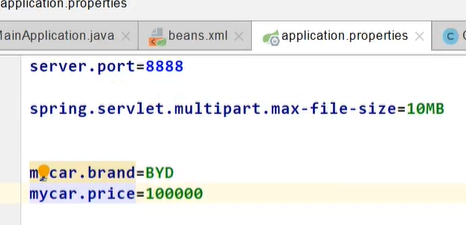

- 在配置类中使用 @EnableConfigurationProperties(Car.class)

3.自动配置原理入门
3.1 源码-引导加载自动配置类
SpringBoot 的核心注解:@SpringBootApplication 等同于三个注解
- @SpringBootConfiguration 本质上就是 @Configuration,代表当前类是一个配置类
- @ComponentScan 指定扫描包
- @EnableAutoConfiguration 它是由两个注解组成的
@AutoConfigurationPackage
@Import(AutoConfigurationImportSelector.class)
public @interface EnableAutoConfiguration {}
- @AutoConfigurationPackage自动配置包,指定了默认的包规则
@Import(AutoConfigurationPackages.Registrar.class) //给容器中导入一个组件
public @interface AutoConfigurationPackage {}
//利用Registrar给容器中导入一系列组件
//将指定的一个包下的所有组件导入进来?MainApplication 所在包下。
- @Import(AutoConfigurationImportSelector.class)
1、利用getAutoConfigurationEntry(annotationMetadata);给容器中批量导入一些组件
2、调用List<String> configurations = getCandidateConfigurations(annotationMetadata, attributes)获取到所有需要导入到容器中的配置类
3、利用工厂加载 Map<String, List<String>> loadSpringFactories(@Nullable ClassLoader classLoader);得到所有的组件
4、从META-INF/spring.factories位置来加载一个文件。
默认扫描我们当前系统里面所有META-INF/spring.factories位置的文件
spring-boot-autoconfigure-2.3.4.RELEASE.jar包里面也有META-INF/spring.factories
这个文件中写死了spring-boot一启动就要给容器加载的所有配置类3.2 源码-按需开启自动配置项
虽然我们127个场景的所有自动配置启动的时候默认全部加载,但是最终会按需配置
-按照条件装配@Conditional进行按需配置3.3 源码-定制化修改自动配置
SpringBoot 默认会在底层配好所有的组件,但是如果用户自己配置了以用户的优先,因为 @ConditionalOnMissingBean
总结:
SpringBoot 先加载所有的自动配置类 xxxAutoConfiguration
每个自动配置类按照条件进行生效,默认都会绑定配置文件指定的值 xxxProperties
生效的配置类就会给容器中装配很多组件
只要容器中有这些组件,相当于这些功能就有了
定制化配置
- 用户直接自己 @Bean 替换底层的组件
- 用户去看这个组件时获取的配置文件什么值就去修改
xxxAutoConfiguration--->组件--->xxxProperties 中取值--->application.properties
3.4 最佳实践
引入场景依赖
- 官方文档
查看自动配置做了哪些(选做)
- 自己分析,引入场景对应的自动配置一般都生效了
- 配置文件中 debug=true 开启自动配置报告。Negative(不生效)/ Positive(生效)
是否需要修改
参照文档修改配置项
- 参照官方文档
- 自己分析,xxxProperties 绑定了配置文件的哪些
自定义加入或替换组件
- @Bean、@Component
自定义器 xxxCustomizer
4.开发技巧
4.1 Lombok
简化 JavaBean 开发
步骤:1.引入依赖 2.idea 安装 lombok 插件
常用注解:
- @Data:Getter And Setter
- @ToString
- @NoArgsConstructor:无参构造器
- @AllArgsConstructor:全参构造器
- @EqualsAndHashCode
- @Slf4j:简化日志开发
4.2 dev-tools
开发者工具-热更新(重新编译一下,如果是静态页面不用重启,静态替换一下。真正的热更新付费的)
Ctrl+F9
4.3 Spring Initailizr(项目初始化向导)
- 自动依赖引入
- 自动创建项目结构
- 自动编写好主配置类
第一季:SpringBoot2 核心技术-核心功能
04、配置文件
1、文件类型
1.1、properties
同以前的 properties 用法
1.2、yaml
1.2.1、简介
YAML 是 "YAML Ain't Markup Language"(YAML 不是一种标记语言)的递归缩写。在开发的这种语言时,YAML 的意思其实是:"Yet Another Markup Language"(仍是一种标记语言)。
非常适合用来做以数据为中心的配置文件
1.2.2、基本语法
- key: value;kv 之间有空格
- 大小写敏感
- 使用缩进表示层级关系
- 缩进不允许使用 tab,只允许空格
- 缩进的空格数不重要,只要相同层级的元素左对齐即可
- '#'表示注释
- 字符串无需加引号,如果要加,''与""表示字符串内容 会被 转义/不转义
1.2.3、数据类型
- 字面量:单个的、不可再分的值。date、boolean、string、number、null
k: v- 对象:键值对的集合。map、hash、set、object
行内写法: k: {k1:v1,k2:v2,k3:v3}
#或
k:
k1: v1
k2: v2
k3: v3- 数组:一组按次序排列的值。array、list、queue
行内写法: k: [v1,v2,v3]
#或者
k:
- v1
- v2
- v31.2.4、示例
@Data
public class Person {
private String userName;
private Boolean boss;
private Date birth;
private Integer age;
private Pet pet;
private String[] interests;
private List<String> animal;
private Map<String, Object> score;
private Set<Double> salarys;
private Map<String, List<Pet>> allPets;
}
@Data
public class Pet {
private String name;
private Double weight;
}
# yaml表示以上对象
person:
userName: zhangsan
boss: false
birth: 2019/12/12 20:12:33
age: 18
pet:
name: tomcat
weight: 23.4
interests: [篮球,游泳]
animal:
- jerry
- mario
score:
english:
first: 30
second: 40
third: 50
math: [131,140,148]
chinese: {first: 128,second: 136}
salarys: [3999,4999.98,5999.99]
allPets:
sick:
- {name: tom}
- {name: jerry,weight: 47}
health: [{name: mario,weight: 47}]
2.配置提示
自定义的 JavaBean 绑定配置文件,写配置的时候一般没有提示,参照文档添加依赖
// 配置提示
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-configuration-processor</artifactId>
<optional>true</optional>
</dependency>
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId>
// 打包时不打包这个依赖
<configuration>
<excludes>
<exclude>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-configuration-processor</artifactId>
</exclude>
</excludes>
</configuration>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>05、Web 开发
1.SpringMVC 自动配置概览
参照官方文档 Spirng Boot Features 7.Developing Web Application
2.简单功能分析
- 通过 Spring Initializr 创建项目
- 设置包名、jdk
- 勾选 Web、lombok、DevTools、configuration processer
- **删除没用的文件:.mvn, .gitignore, **HELP.md, mvnw, mvnw.cmd
- 新建 application.yml
2.1 静态资源访问
2.1.1 静态资源目录
参照官方文档 7.1.5,静态资源目录:类路径(resources)下的这几个文件夹 static、public、resources、META-INF/resources 访问静态资源:当前项目根路径/+ 静态资源名
**原理:静态资源的映射是 **"/**",请求进来,会先去找 Controller 看能不能处理(动态请求),不能处理的所有请求又都交给静态资源处理器。静态资源也找不到则响应 404
2.1.2 配置静态资源访问前缀和路径
一般为拦截器配置放行,给静态资源配置访问前缀,默认无前缀,在配置文件中进行配置
spring:
mvc:
static-path-pattern: /res/**
resources:
static-locations: [classpath:/haha/]2.1.3 webjar
webjar:将 web 端静态资源打成 jar 包,可以去 webjar 官网找对应的依赖,比如 jquery
然后通过静态目录/webjars/进行访问
2.2 欢迎页
官方文档 7.1.6 Welcome Page
欢迎页两种设置方法:
静态资源路径下 index.html
- 可以配置静态资源路径,但是不可以配置静态资源的访问前缀,否则 index.html 不能被默认访问
controller 能处理 /index
2.3 自定义 Favcion
favicon.ico 放在静态资源目录下即可。配置静态资源的访问前缀依旧会导致失效
2.4 源码-静态资源配置原理
- SpringBoot 启动默认加载 xxxAutoConfiguration 类(自动配置类)
- SpringMVC 功能的自动配置类 WebMvcAutoConfiguration,查看是否生效
-
@Configuration(proxyBeanMethods = false)
@ConditionalOnWebApplication(type = Type.SERVLET)
@ConditionalOnClass({ Servlet.class, DispatcherServlet.class, WebMvcConfigurer.class })
@ConditionalOnMissingBean(WebMvcConfigurationSupport.class)
@AutoConfigureOrder(Ordered.HIGHEST_PRECEDENCE + 10)
@AutoConfigureAfter({ DispatcherServletAutoConfiguration.class, TaskExecutionAutoConfiguration.class,
ValidationAutoConfiguration.class })
public class WebMvcAutoConfiguration {}- 查看给容器中配置了什么,可以找内部配置类
-
@Configuration(proxyBeanMethods = false)
@Import(EnableWebMvcConfiguration.class)
@EnableConfigurationProperties({ WebMvcProperties.class, ResourceProperties.class })
@Order(0)
public static class WebMvcAutoConfigurationAdapter implements WebMvcConfigurer {}- 发现配置文件的相关属性和 xxx 进行了绑定。WebMvcPropertiesspring.mvc、ResourcePropertiesspring.resources
例子:
2.4.1 配置类只有一个有参构造器
//有参构造器所有参数的值都会从容器中确定
//ResourceProperties resourceProperties;获取和spring.resources绑定的所有的值的对象
//WebMvcProperties mvcProperties 获取和spring.mvc绑定的所有的值的对象
//ListableBeanFactory beanFactory Spring的beanFactory
//HttpMessageConverters 找到所有的HttpMessageConverters
//ResourceHandlerRegistrationCustomizer 找到 资源处理器的自定义器。=========
//DispatcherServletPath
//ServletRegistrationBean 给应用注册Servlet、Filter....
public WebMvcAutoConfigurationAdapter(ResourceProperties resourceProperties, WebMvcProperties mvcProperties,
ListableBeanFactory beanFactory, ObjectProvider<HttpMessageConverters> messageConvertersProvider,
ObjectProvider<ResourceHandlerRegistrationCustomizer> resourceHandlerRegistrationCustomizerProvider,
ObjectProvider<DispatcherServletPath> dispatcherServletPath,
ObjectProvider<ServletRegistrationBean<?>> servletRegistrations) {
this.resourceProperties = resourceProperties;
this.mvcProperties = mvcProperties;
this.beanFactory = beanFactory;
this.messageConvertersProvider = messageConvertersProvider;
this.resourceHandlerRegistrationCustomizer = resourceHandlerRegistrationCustomizerProvider.getIfAvailable();
this.dispatcherServletPath = dispatcherServletPath;
this.servletRegistrations = servletRegistrations;
}2.4.2 资源处理的默认规则
@Override
public void addResourceHandlers(ResourceHandlerRegistry registry) {
if (!this.resourceProperties.isAddMappings()) {
logger.debug("Default resource handling disabled");
return;
}
Duration cachePeriod = this.resourceProperties.getCache().getPeriod();
CacheControl cacheControl = this.resourceProperties.getCache().getCachecontrol().toHttpCacheControl();
//webjars的规则
if (!registry.hasMappingForPattern("/webjars/**")) {
customizeResourceHandlerRegistration(registry.addResourceHandler("/webjars/**")
.addResourceLocations("classpath:/META-INF/resources/webjars/")
.setCachePeriod(getSeconds(cachePeriod)).setCacheControl(cacheControl));
}
//
String staticPathPattern = this.mvcProperties.getStaticPathPattern();
if (!registry.hasMappingForPattern(staticPathPattern)) {
customizeResourceHandlerRegistration(registry.addResourceHandler(staticPathPattern)
.addResourceLocations(getResourceLocations(this.resourceProperties.getStaticLocations()))
.setCachePeriod(getSeconds(cachePeriod)).setCacheControl(cacheControl));
}
}
spring:
# mvc:
# static-path-pattern: /res/**
resources:
add-mappings: false 禁用所有静态资源规则
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "spring.resources", ignoreUnknownFields = false)
public class ResourceProperties {
private static final String[] CLASSPATH_RESOURCE_LOCATIONS = { "classpath:/META-INF/resources/",
"classpath:/resources/", "classpath:/static/", "classpath:/public/" };
/**
* Locations of static resources. Defaults to classpath:[/META-INF/resources/,
* /resources/, /static/, /public/].
*/
private String[] staticLocations = CLASSPATH_RESOURCE_LOCATIONS;2.4.3 欢迎页的处理规则
HandlerMapping:处理器映射。保存了每一个Handler能处理哪些请求。
@Bean
public WelcomePageHandlerMapping welcomePageHandlerMapping(ApplicationContext applicationContext,
FormattingConversionService mvcConversionService, ResourceUrlProvider mvcResourceUrlProvider) {
WelcomePageHandlerMapping welcomePageHandlerMapping = new WelcomePageHandlerMapping(
new TemplateAvailabilityProviders(applicationContext), applicationContext, getWelcomePage(),
this.mvcProperties.getStaticPathPattern());
welcomePageHandlerMapping.setInterceptors(getInterceptors(mvcConversionService, mvcResourceUrlProvider));
welcomePageHandlerMapping.setCorsConfigurations(getCorsConfigurations());
return welcomePageHandlerMapping;
}
WelcomePageHandlerMapping(TemplateAvailabilityProviders templateAvailabilityProviders,
ApplicationContext applicationContext, Optional<Resource> welcomePage, String staticPathPattern) {
if (welcomePage.isPresent() && "/**".equals(staticPathPattern)) {
//要用欢迎页功能,必须是/**
logger.info("Adding welcome page: " + welcomePage.get());
setRootViewName("forward:index.html");
}
else if (welcomeTemplateExists(templateAvailabilityProviders, applicationContext)) {
// 调用Controller /index
logger.info("Adding welcome page template: index");
setRootViewName("index");
}
}2.4.4 favicon
3.请求参数处理
3.1 源码-请求映射
@xxxMapping;
Rest 风格支持(使用 HTTP 请求方式动词来表示对资源的操作) 以前:/getUser/deleteUser/editUser/saveUser 现在:/user ** GET** DELETEPUTPOST
核心在于 Filter:HiddenHttpMethodFilter
- 用法:表单 method=post,隐藏域_method=put
- 在 SpringBoot 中手动开启
3.1.1 Rest 原理(表单提交要使用 REST 的时候)
表单提交会带上_method=PUT
请求过来被 HiddenHttpMethodFilter 拦截
请求是否正常,并且是 POST
* **获取到_method 的值。**
* **兼容以下请求;PUT.DELETE.PATCH**
* **原生 request(post),包装模式 requesWrapper 重写了 getMethod 方法,返回的是传入的值。**
* **过滤器链放行的时候用 wrapper。以后的方法调用 getMethod 是调用 requesWrapper 的。**
Rest 使用客户端工具
- 如 PostMan 直接发送 Put、delete 等方式请求,无需 Filter。
代码示例
@RequestMapping(value = "/user",method = RequestMethod.GET)
public String getUser(){
return "GET-张三";
}
@RequestMapping(value = "/user",method = RequestMethod.POST)
public String saveUser(){
return "POST-张三";
}
@RequestMapping(value = "/user",method = RequestMethod.PUT)
public String putUser(){
return "PUT-张三";
}
@RequestMapping(value = "/user",method = RequestMethod.DELETE)
public String deleteUser(){
return "DELETE-张三";
}
@Bean
@ConditionalOnMissingBean(HiddenHttpMethodFilter.class)
@ConditionalOnProperty(prefix = "spring.mvc.hiddenmethod.filter", name = "enabled", matchIfMissing = false)
public OrderedHiddenHttpMethodFilter hiddenHttpMethodFilter() {
return new OrderedHiddenHttpMethodFilter();
}
//自定义filter
@Bean
public HiddenHttpMethodFilter hiddenHttpMethodFilter(){
HiddenHttpMethodFilter methodFilter = new HiddenHttpMethodFilter();
methodFilter.setMethodParam("_m");
return methodFilter;
}
spring:
mvc:
hiddenmethod:
filter:
enabled: true #开启页面表单的Rest功能3.2 源码-请求映射原理
ctrl+F12 打开结构树
DispatcherServlet 是处理所有请求的开始,它本身是一个 Servlet,作为 Servlet,肯定要重写 doGet 和 doPost 方法
通过继承树找那个 Servlet 重写了 doGet、doPost……
最终 DispatcherServlet 最 doService 进行了实现,最终应该分析 doDispatch 方法
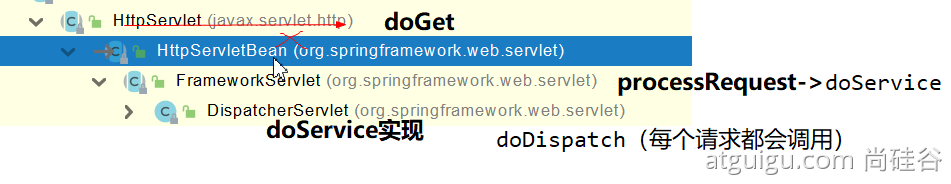
SpringMVC 功能分析都从 org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet-》doDispatch()
protected void doDispatch(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception {
HttpServletRequest processedRequest = request;
HandlerExecutionChain mappedHandler = null;
boolean multipartRequestParsed = false;
WebAsyncManager asyncManager = WebAsyncUtils.getAsyncManager(request);
try {
ModelAndView mv = null;
Exception dispatchException = null;
try {
processedRequest = checkMultipart(request);
multipartRequestParsed = (processedRequest != request);
// 找到当前请求使用哪个Handler(Controller的方法)处理
mappedHandler = getHandler(processedRequest);
//HandlerMapping:处理器映射。/xxx->>xxxx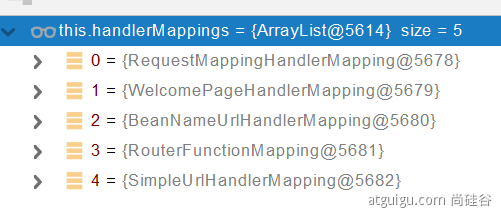
RequestMappingHandlerMapping
:保存了所有 @RequestMapping 和 handler 的映射规则。
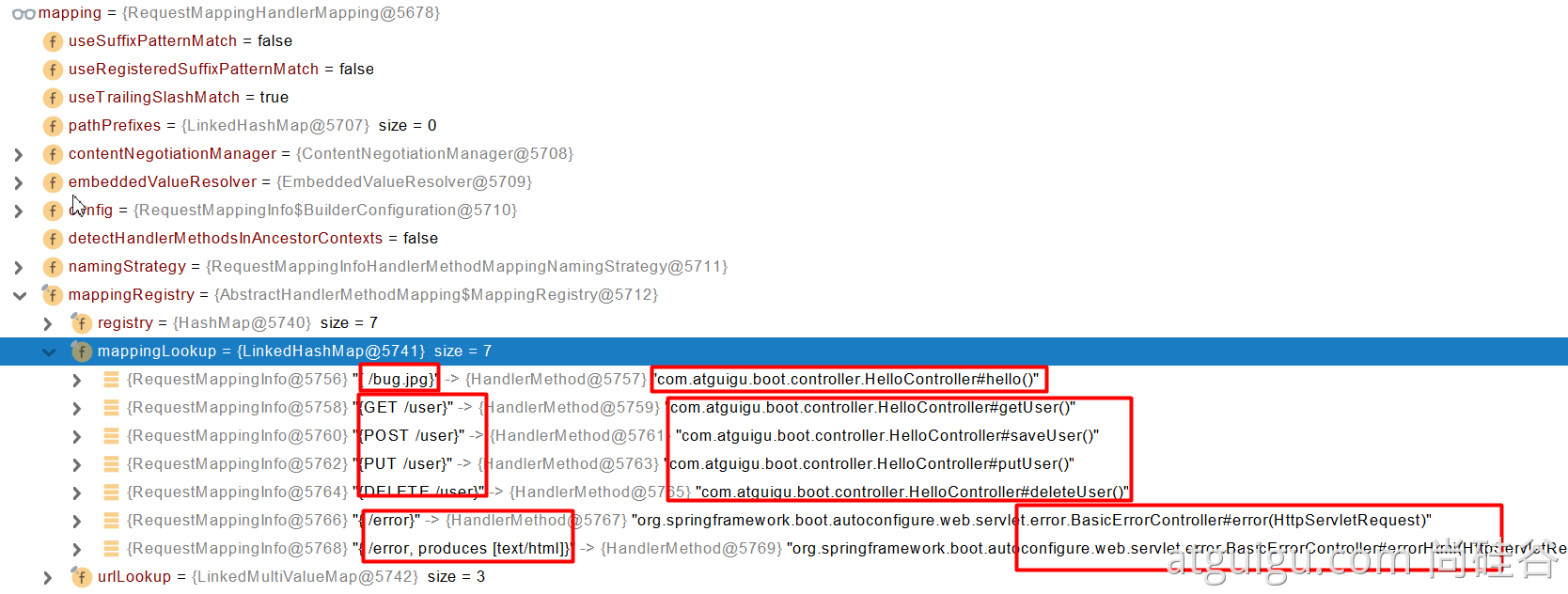
所有的请求映射都在 HandlerMapping 中。
SpringBoot 自动配置欢迎页的 WelcomePageHandlerMapping 。访问 /能访问到 index.html;
SpringBoot 自动配置了默认 的 RequestMappingHandlerMapping
请求进来,挨个尝试所有的 HandlerMapping 看是否有请求信息。
如果有就找到这个请求对应的 handler
如果没有就是下一个 HandlerMapping
我们需要一些自定义的映射处理,我们也可以自己给容器中放****HandlerMapping。自定义 HandlerMapping
protected HandlerExecutionChain getHandler(HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception {
if (this.handlerMappings != null) {
for (HandlerMapping mapping : this.handlerMappings) {
HandlerExecutionChain handler = mapping.getHandler(request);
if (handler != null) {
return handler;
}
}
}
return null;
}3.3 普通参数与基本注解
SpringMVC 在底层接收 Web 请求可以处理的传参类型
3.3.1 注解
一般在请求域中放入数据然后跳转到页面,在页面用表达式获取
@PathVariable(路径变量)
@GetMapping("/car/{id}/owner/{username}")
@PathVariable("id") Integer id,
@PathVariable("username") String name,
@PathVariable Map<String,String> pv,
@RequestHeader(获取请求头)
@RequestHeader("User-Agent") String userAgent,
@RequestHeader Map<String,String> header,
@RequestParam(获取请求参数)
@GetMapping("/user?age=11&inters=aa&inters=bb")
@RequestParam("age") Integer age,
@RequestParam("inters") List<String> inters,
@RequestParam Map<String,String> params,
@CookieValue(获取cookie值)
@CookieValue("_ga") String _ga,
@CookieValue("_ga") Cookie cookie
@RequestBody(获取请求体[POST],一般用于表单)
@PostMapping("/save")
@RequestBody String content
@RequestAttribute(获取request域中的值)
一般给request域设置属性,用来页面转发的时候可以取出当前请求的数据
如果只是@Controller,返回的数据是用来页面跳转的
要取出请求域中的数据,必须是转发(重定向forward)
示例代码:
@GetMapping("goto")
public String goToPage(HttpServletRequest Request){
request.setAttribute("msg","successed");
request.setAttribute("code","200");
return "forward:/success"
}
@ResponseBody
@GetMapping("/success")
public Map success(@RequestAttribute("msg") String msg,
@RequestAttribute("code" Integer code,
HttpServletRequest request)){
/*more code*/
}
@MatrixVariable(矩阵变量)
//作用示例:页面开发,cookie禁用了,session里面的内容怎么使用?
//session对象通过jsessionid=xxx找到,jsessionid存放在cookie中,每次发请求的时候携带cookie
//cookie禁用后,可以重写url,通过矩阵变量的方式传递jsessionid
//1、语法: 请求路径:/cars/sell;low=34;brand=byd,audi,yd
//2、SpringBoot默认是禁用了矩阵变量的功能
// 手动开启:原理。对于路径的处理。UrlPathHelper进行解析。
// removeSemicolonContent(移除分号内容)支持矩阵变量的
//3、矩阵变量必须有url路径变量才能被解析
@GetMapping("/cars/{path}")
public Map carsSell(@MatrixVariable("low") Integer low,
@MatrixVariable("brand") List<String> brand,
@PathVariable("path") String path){
Map<String,Object> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("low",low);
map.put("brand",brand);
map.put("path",path);
return map;
}
// /boss/1;age=20/2;age=10
@GetMapping("/boss/{bossId}/{empId}")
public Map boss(@MatrixVariable(value = "age",pathVar = "bossId") Integer bossAge,
@MatrixVariable(value = "age",pathVar = "empId") Integer empAge){
Map<String,Object> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("bossAge",bossAge);
map.put("empAge",empAge);
return map;
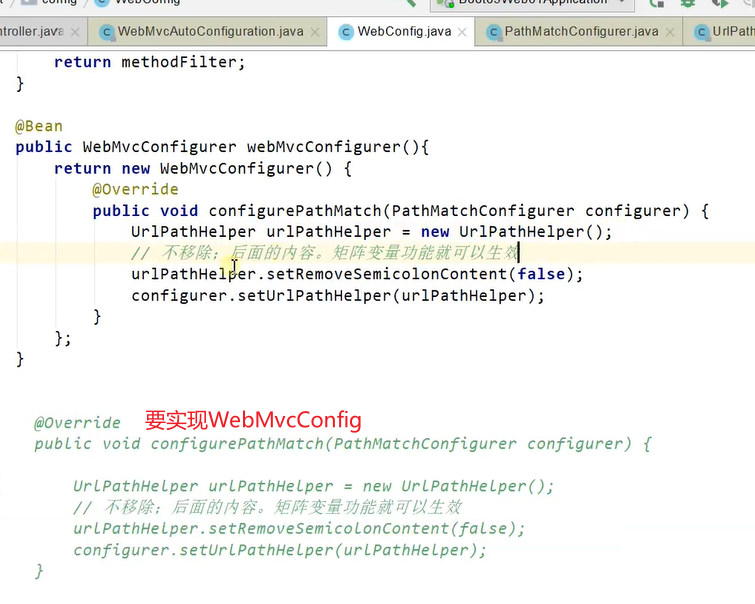
}开启矩阵变量的配置方法:
3.3.2 Servlet API:
WebRequest、ServletRequest、MultipartRequest、 HttpSession、javax.servlet.http.PushBuilder、Principal、InputStream、Reader、HttpMethod、Locale、TimeZone、ZoneId
ServletRequestMethodArgumentResolver 以上的部分参数
@Override
public boolean supportsParameter(MethodParameter parameter) {
Class<?> paramType = parameter.getParameterType();
return (WebRequest.class.isAssignableFrom(paramType) ||
ServletRequest.class.isAssignableFrom(paramType) ||
MultipartRequest.class.isAssignableFrom(paramType) ||
HttpSession.class.isAssignableFrom(paramType) ||
(pushBuilder != null && pushBuilder.isAssignableFrom(paramType)) ||
Principal.class.isAssignableFrom(paramType) ||
InputStream.class.isAssignableFrom(paramType) ||
Reader.class.isAssignableFrom(paramType) ||
HttpMethod.class == paramType ||
Locale.class == paramType ||
TimeZone.class == paramType ||
ZoneId.class == paramType);
}所有参数最后都是 resolver 解析
3.3.3 复杂参数
Map、Model(map、model 里面的数据会被默认放在 request 的请求域 request.setAttribute)、 Errors/BindingResult、RedirectAttributes( 重定向携带数据) 、ServletResponse(response) 、SessionStatus、UriComponentsBuilder、ServletUriComponentsBuilder
Map<String,Object> map, Model model, HttpServletRequest request 都是可以给request域中放数据,
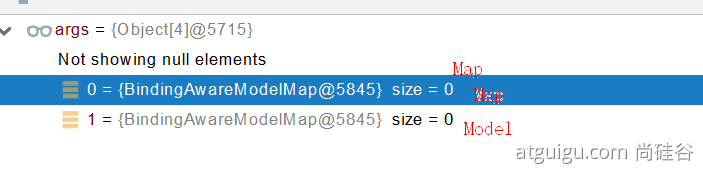
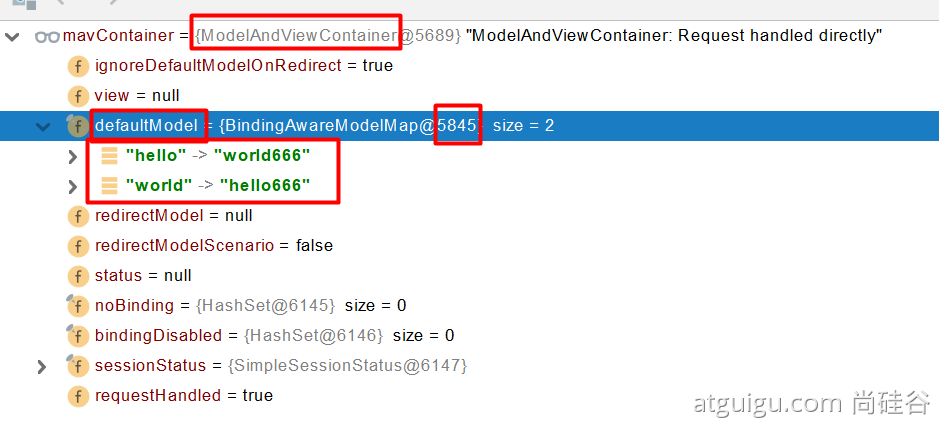
request.getAttribute();Map、Model 类型的参数,会返回 mavContainer.getModel();---> BindingAwareModelMap 是 Model 也是 Map
mavContainer.getModel(); 获取到值的
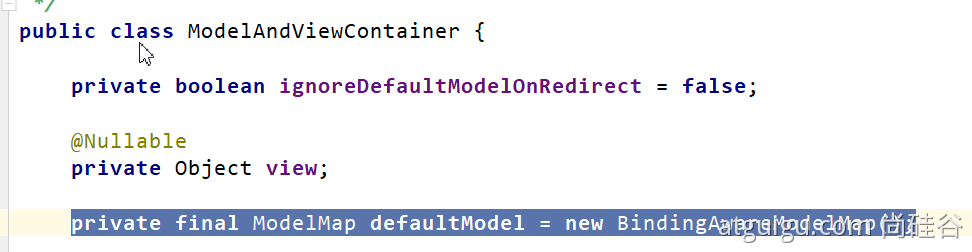
3.3.4 自定义对象参数
可以自动类型转换与格式化,可以级联封装。
/**
* 姓名: <input name="userName"/>
* 年龄: <input name="age"/>
* 生日: <input name="birth"/>
* 宠物姓名:<input name="pet.name"/><br/>
* 宠物年龄:<input name="pet.age"/>
*/
@Data
public class Person {
private String userName;
private Integer age;
private Date birth;
private Pet pet;
}
@Data
public class Pet {
private String name;
private String age;
}
result3.4 POJO 封装过程
- ServletModelAttributeMethodProcessor
3.5 源码-参数处理原理:
根据注解,自动确定值和源码的过程原理
所有的源码肯定是从 DispatcherServlet 开始,因为这是处理请求的整个入口
DispatcherServlet--->doDispatche()--->mappedHandler--->HandlerMappings--->HandlerAdapter(封装大的反射工具用来调用 Controller 方法)--->执行目标方法
- HandlerMapping 中找到能处理请求的 Handler(Controller.method())
- **为当前 Handler 找一个适配器 HandlerAdapter; **RequestMappingHandlerAdapter
- 适配器执行目标方法并确定方法参数的每一个值
3.5.1 HandlerAdapter
-
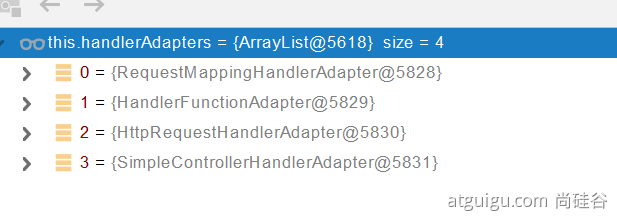
- 0 - 支持方法上标注 @RequestMapping 1 - 支持函数式编程的 xxxxxx
3.5.2 执行目标方法
// Actually invoke the handler.
//DispatcherServlet -- doDispatch
mv = ha.handle(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler.getHandler());
mav = invokeHandlerMethod(request, response, handlerMethod); //执行目标方法
//第一步
//ServletInvocableHandlerMethod
Object returnValue = invokeForRequest(webRequest, mavContainer, providedArgs);
//第二步获取方法的参数值
Object[] args = getMethodArgumentValues(request, mavContainer, providedArgs);3.5.3 参数解析器-HandlerMethodArgumentResolver
确定将要执行的目标方法的每一个参数的值是什么; SpringMVC 目标方法能写多少种参数类型。取决于参数解析器。

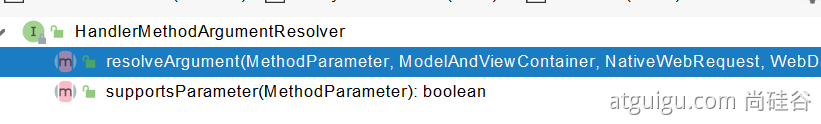
- 当前解析器是否支持解析这种参数
- 支持就调用解析方法 resolveArgument
3.5.4 返回值处理器
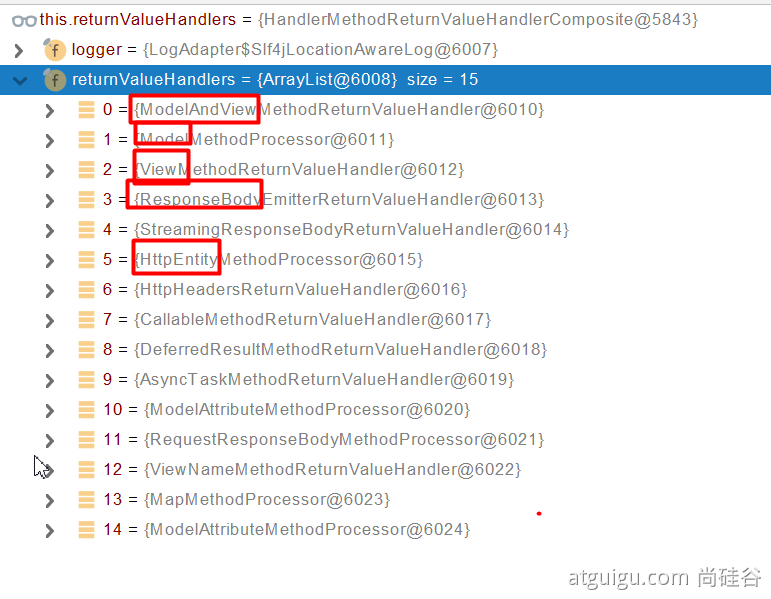
3.5.5 如何确定目标方法每一个参数的值
============InvocableHandlerMethod==========================
protected Object[] getMethodArgumentValues(NativeWebRequest request, @Nullable ModelAndViewContainer mavContainer,
Object... providedArgs) throws Exception {
MethodParameter[] parameters = getMethodParameters();
if (ObjectUtils.isEmpty(parameters)) {
return EMPTY_ARGS;
}
Object[] args = new Object[parameters.length];
for (int i = 0; i < parameters.length; i++) {
MethodParameter parameter = parameters[i];
parameter.initParameterNameDiscovery(this.parameterNameDiscoverer);
args[i] = findProvidedArgument(parameter, providedArgs);
if (args[i] != null) {
continue;
}
if (!this.resolvers.supportsParameter(parameter)) {
throw new IllegalStateException(formatArgumentError(parameter, "No suitable resolver"));
}
try {
args[i] = this.resolvers.resolveArgument(parameter, mavContainer, request, this.dataBinderFactory);
}
catch (Exception ex) {
// Leave stack trace for later, exception may actually be resolved and handled...
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
String exMsg = ex.getMessage();
if (exMsg != null && !exMsg.contains(parameter.getExecutable().toGenericString())) {
logger.debug(formatArgumentError(parameter, exMsg));
}
}
throw ex;
}
}
return args;
}- 挨个判断所有参数解析器那个支持解析这个参数解析这个参数的值
@Nullable
private HandlerMethodArgumentResolver getArgumentResolver(MethodParameter parameter) {
HandlerMethodArgumentResolver result = this.argumentResolverCache.get(parameter);
if (result == null) {
for (HandlerMethodArgumentResolver resolver : this.argumentResolvers) {
if (resolver.supportsParameter(parameter)) {
result = resolver;
this.argumentResolverCache.put(parameter, result);
break;
}
}
}
return result;
}- 解析这个参数的值
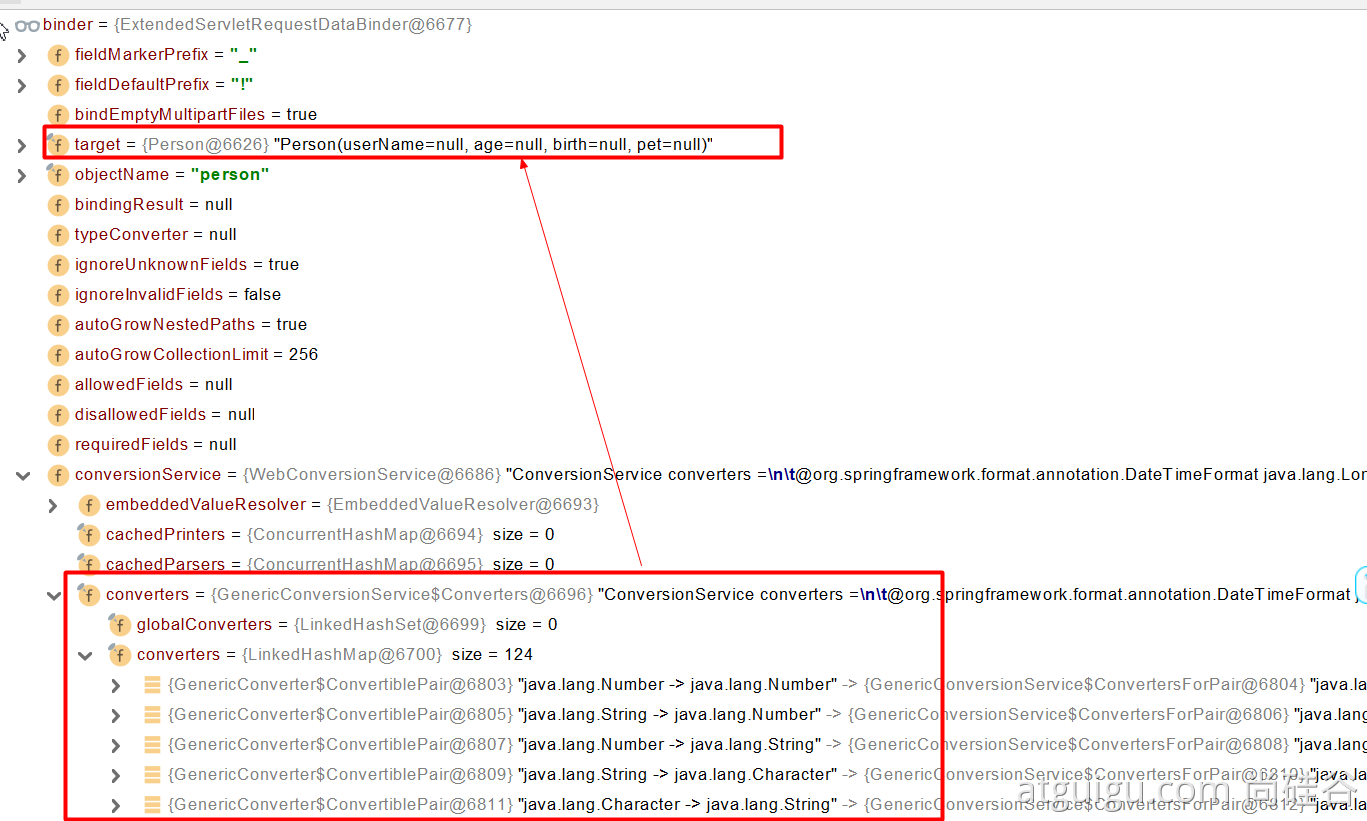
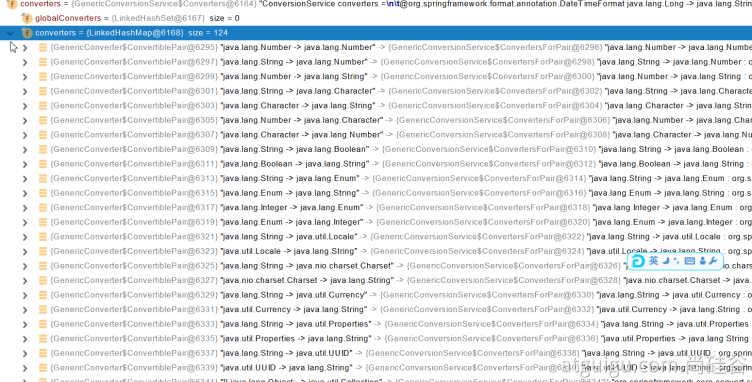
调用各自 HandlerMethodArgumentResolver 的 resolveArgument 方法即可- 自定义类型参数 封装 POJO ServletModelAttributeMethodProcessor 这个参数处理器支持是否为简单类型。 WebDataBinder binder = binderFactory.createBinder(webRequest, attribute, name); WebDataBinder :web 数据绑定器,将请求参数的值绑定到指定的 JavaBean 里面 WebDataBinder 利用它里面的 Converters 将请求数据转成指定的数据类型。再次封装到 JavaBean 中 GenericConversionService:在设置每一个值的时候,找它里面的所有 converter 那个可以将这个数据类型(request 带来参数的字符串)转换到指定的类型(JavaBean -- Integer) byte -- > file @FunctionalInterfacepublic interface Converter<S, T>
**未来我们可以给 WebDataBinder 里面放自己的 Converter; **private static final class StringToNumber<T extends Number> implements Converter<String, T> 自定义 Converter
public static boolean isSimpleValueType(Class<?> type) {
return (Void.class != type && void.class != type &&
(ClassUtils.isPrimitiveOrWrapper(type) ||
Enum.class.isAssignableFrom(type) ||
CharSequence.class.isAssignableFrom(type) ||
Number.class.isAssignableFrom(type) ||
Date.class.isAssignableFrom(type) ||
Temporal.class.isAssignableFrom(type) ||
URI.class == type ||
URL.class == type ||
Locale.class == type ||
Class.class == type));
}
@Override
@Nullable
public final Object resolveArgument(MethodParameter parameter, @Nullable ModelAndViewContainer mavContainer,
NativeWebRequest webRequest, @Nullable WebDataBinderFactory binderFactory) throws Exception {
Assert.state(mavContainer != null, "ModelAttributeMethodProcessor requires ModelAndViewContainer");
Assert.state(binderFactory != null, "ModelAttributeMethodProcessor requires WebDataBinderFactory");
String name = ModelFactory.getNameForParameter(parameter);
ModelAttribute ann = parameter.getParameterAnnotation(ModelAttribute.class);
if (ann != null) {
mavContainer.setBinding(name, ann.binding());
}
Object attribute = null;
BindingResult bindingResult = null;
if (mavContainer.containsAttribute(name)) {
attribute = mavContainer.getModel().get(name);
}
else {
// Create attribute instance
try {
attribute = createAttribute(name, parameter, binderFactory, webRequest);
}
catch (BindException ex) {
if (isBindExceptionRequired(parameter)) {
// No BindingResult parameter -> fail with BindException
throw ex;
}
// Otherwise, expose null/empty value and associated BindingResult
if (parameter.getParameterType() == Optional.class) {
attribute = Optional.empty();
}
bindingResult = ex.getBindingResult();
}
}
if (bindingResult == null) {
// Bean property binding and validation;
// skipped in case of binding failure on construction.
WebDataBinder binder = binderFactory.createBinder(webRequest, attribute, name);
if (binder.getTarget() != null) {
if (!mavContainer.isBindingDisabled(name)) {
bindRequestParameters(binder, webRequest);
}
validateIfApplicable(binder, parameter);
if (binder.getBindingResult().hasErrors() && isBindExceptionRequired(binder, parameter)) {
throw new BindException(binder.getBindingResult());
}
}
// Value type adaptation, also covering java.util.Optional
if (!parameter.getParameterType().isInstance(attribute)) {
attribute = binder.convertIfNecessary(binder.getTarget(), parameter.getParameterType(), parameter);
}
bindingResult = binder.getBindingResult();
}
// Add resolved attribute and BindingResult at the end of the model
Map<String, Object> bindingResultModel = bindingResult.getModel();
mavContainer.removeAttributes(bindingResultModel);
mavContainer.addAllAttributes(bindingResultModel);
return attribute;
}
//1、WebMvcConfigurer定制化SpringMVC的功能
@Bean
public WebMvcConfigurer webMvcConfigurer(){
return new WebMvcConfigurer() {
@Override
public void configurePathMatch(PathMatchConfigurer configurer) {
UrlPathHelper urlPathHelper = new UrlPathHelper();
// 不移除;后面的内容。矩阵变量功能就可以生效
urlPathHelper.setRemoveSemicolonContent(false);
configurer.setUrlPathHelper(urlPathHelper);
}
@Override
public void addFormatters(FormatterRegistry registry) {
registry.addConverter(new Converter<String, Pet>() {
@Override
public Pet convert(String source) {
// 啊猫,3
if(!StringUtils.isEmpty(source)){
Pet pet = new Pet();
String[] split = source.split(",");
pet.setName(split[0]);
pet.setAge(Integer.parseInt(split[1]));
return pet;
}
return null;
}
});
}
};
}3.6 目标方法执行完成
将所有的数据都放在 ModelAndViewContainer;包含要去的页面地址 View。还包含 Model 数据。
3.7 处理派发结果
processDispatchResult(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler, mv, dispatchException);
renderMergedOutputModel(mergedModel, getRequestToExpose(request), response);
InternalResourceView:
@Override
protected void renderMergedOutputModel(
Map<String, Object> model, HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception {
// Expose the model object as request attributes.
exposeModelAsRequestAttributes(model, request);
// Expose helpers as request attributes, if any.
exposeHelpers(request);
// Determine the path for the request dispatcher.
String dispatcherPath = prepareForRendering(request, response);
// Obtain a RequestDispatcher for the target resource (typically a JSP).
RequestDispatcher rd = getRequestDispatcher(request, dispatcherPath);
if (rd == null) {
throw new ServletException("Could not get RequestDispatcher for [" + getUrl() +
"]: Check that the corresponding file exists within your web application archive!");
}
// If already included or response already committed, perform include, else forward.
if (useInclude(request, response)) {
response.setContentType(getContentType());
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Including [" + getUrl() + "]");
}
rd.include(request, response);
}
else {
// Note: The forwarded resource is supposed to determine the content type itself.
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Forwarding to [" + getUrl() + "]");
}
rd.forward(request, response);
}
}
暴露模型作为请求域属性
// Expose the model object as request attributes.
exposeModelAsRequestAttributes(model, request);
protected void exposeModelAsRequestAttributes(Map<String, Object> model,
HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception {
//model中的所有数据遍历挨个放在请求域中
model.forEach((name, value) -> {
if (value != null) {
request.setAttribute(name, value);
}
else {
request.removeAttribute(name);
}
});
}